A multispectral light sources based tissue oxygenation imaging system for telemedicine wound healing phases recognition
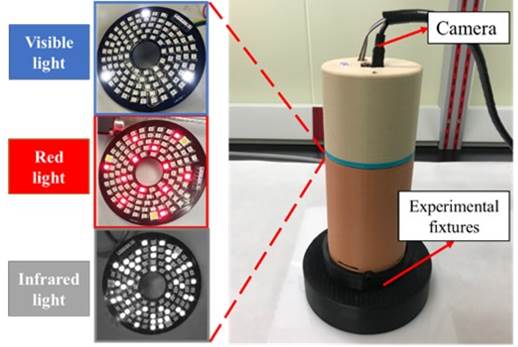
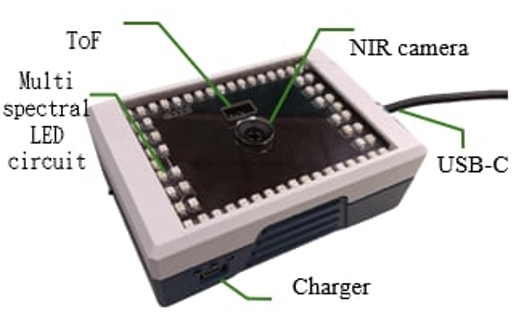
This research cooperates with Taiwan Instrument Research Institute, NARLabs and BenQ Materials Corporation, and develops a multispectral image recognition system to detect blood tissue oxygenation of subcutaneous tissues. The light penetrability of skin tissue and the light absorption of hemoglobin are analyzed to establish different transfer models for high precision blood oxygen distribution. Furthermore, Deep learning-based image recognition algorithms are developed to determine the healing stages of wounds and produce wound information. Besides, this research also combines with dressings produced by BenQ Materials Corporation to accelerate wound recovery. For the purpose of telemedicine, the Internet of Things and the cloud database are applied to the imaging system to establish a cloud-based tracking platform, which tracks the recovery of patients’ wounds at home by using mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. To verify the validity of the imaging system, this research collaborates with National Cheng Kung University Hospital to operate animal experiments and clinical experiments and apply for medical materials certification. Moreover, the concept of human factors engineering is adopted in designing human-computer interaction interfaces and ambient light masks to improve user experiences. The prototype products are conducted in clinical field trials in cooperative medical institutions, and user feedback is collected to optimize the imaging system. This system has currently obtained a Taiwan invention patent and a U.S. provisional patent and has a U.S. invention patent under review. Moreover, this system won the Diamond Award and the Best Creative Award in the Macronix Golden Silicon Awards in 2023 and won the 2023 National Innovation Award-Academic Research Innovation Award.
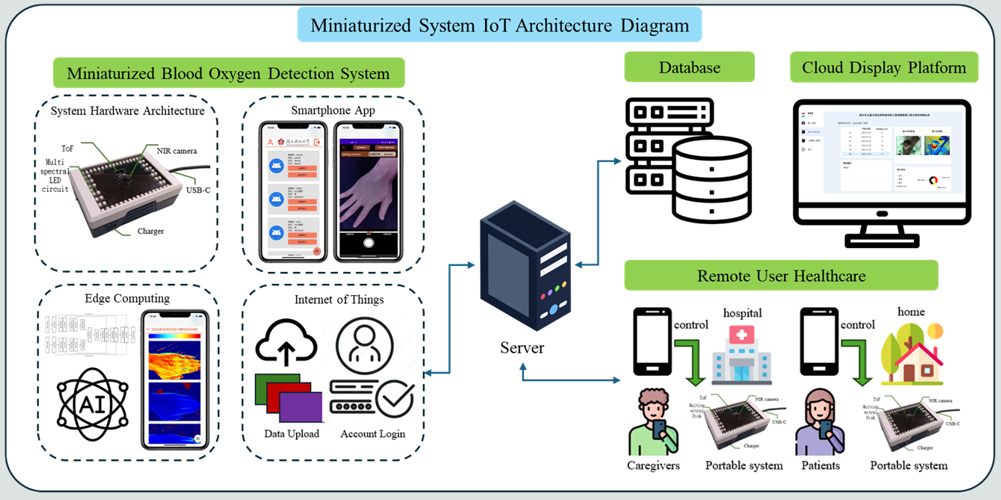
Figure 1. Architecture diagram of multispectral imaging system